Sepsis is the sum of life-threatening disease symptoms and pathophysiological changes caused by microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites) and their products (PAMPs, pathogen-associated microbial patterns) gaining access to the bloodstream from a focus of infection. The body responds by forming endogenous mediators (cytokines), which activate inflammation cascades. These lead to a systemic inflammation reaction that is no longer under control.
Cell-based test systems for the detection of pyrogenic residues
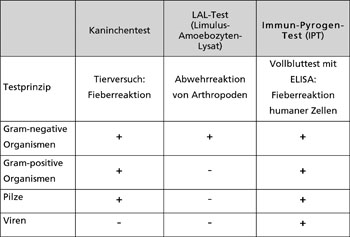
PAMPs, remnants or isolated structures of bacterial pathogens, such as cell wall components of microorganisms, can occur in hospitals and in medical products and devices. Medical equipment that comes into contact with the bloodstream or with large areas of injured tissue must therefore be tested for such pyrogenic residues. There are currently three commercially available methods for the detection of pyrogens (Table 1). These are either very costly, controversial, or limited to specific pyrogens.
New colorimetric assay
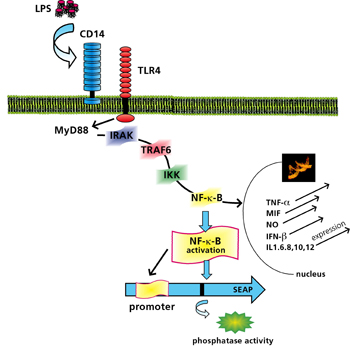
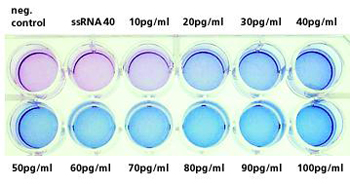
At Fraunhofer IGB we have developed a new, cell-based test system that allows PAMPs to be identified and differentiated via Toll-like receptors (TLRs) [3, 4] (patent applied for). The basis for this is a colorimetric, TLR-induced reporter gene assay (Figure 2) in which positive samples are easily identified by a color reaction. For the assay, the receptor complex comprising Toll-like receptor 4 and coreceptor CD14 (MD2) was stable transfected and expressed in NIH-3T3 fibroblasts containing the reporter gene. The induction of TLRs by an endotoxin (reference substance lipopolysaccharide, LPS) leads, after a signal cascade, to activation of transcription factor NF-kB, which regulates the expression of a secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter gene (Figure 1). In the case of positive samples, addition of substrate leads to the formation of an insoluble deep blue precipitate that is easily detected visually (Figure 2).
Advantages
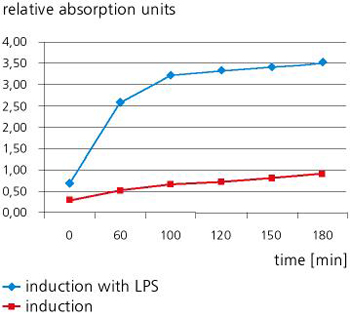
The test system developed in our laboratory allows fast and easy qualitative and quantitative detection of pyrogens without great outlay on equipment. Since the new test system is able to detect and verify all relevant pyrogenic substances that can cause sepsis, it is ideal for use in both medical diagnostics and medical engineering.
Applications and outlook
The new test system can complement or replace existing tests such as LAL and IPT. Pyrogens can be detected on medical equipment, injectable drugs, and on implants or instruments, etc. Other uses are conceivable in the food (pyrogens in foods) and pharmaceutical (pyrogens in medicinal products) industries. TLR antagonists are increasingly used in dermatology.
We intend to extend the test procedure to TLRs 1-10, so that all PAMPs can be selectively detected and identified.
References
[1] Werner-Felmayer, G., Baier-Bitterlich, G., Fuchs, D., Hausen, A., Murr, C., Reibnegger, G., Werner, E. R., Wachter, H. (1995). Detection of bacterial pyrogens on the basis of their effects on gamma interferon-mediated formation of neopterin or nitrite in cultured monocyte cell lines. Clinical and diagnostic laboratory immunology 2(3); 307-313.
[2] J.Jorgensen, J., Alexander, G. A. (1982). Rapid detection of significant bacteriuria by use of an automated Limulus amoebocyte lysat assay. Journal of clinical Microbiology 16(3); 587-589. [12] Akira,S. (2003). Toll-like receptor signaling. J.Biol.Chem. 278, 38105-38108.
[3] Lakhani SA, Bogue CW. (2003). Toll-like receptor signaling in sepsis. Curr Opin Pediatr. 15(3):278-82.
[4] Undurti N. Das. (2003). Current advances in sepsis and septic shock with particular emphasis on the role of insulin. Med Sci Monit 9(8): Ra181-192.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB
Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB